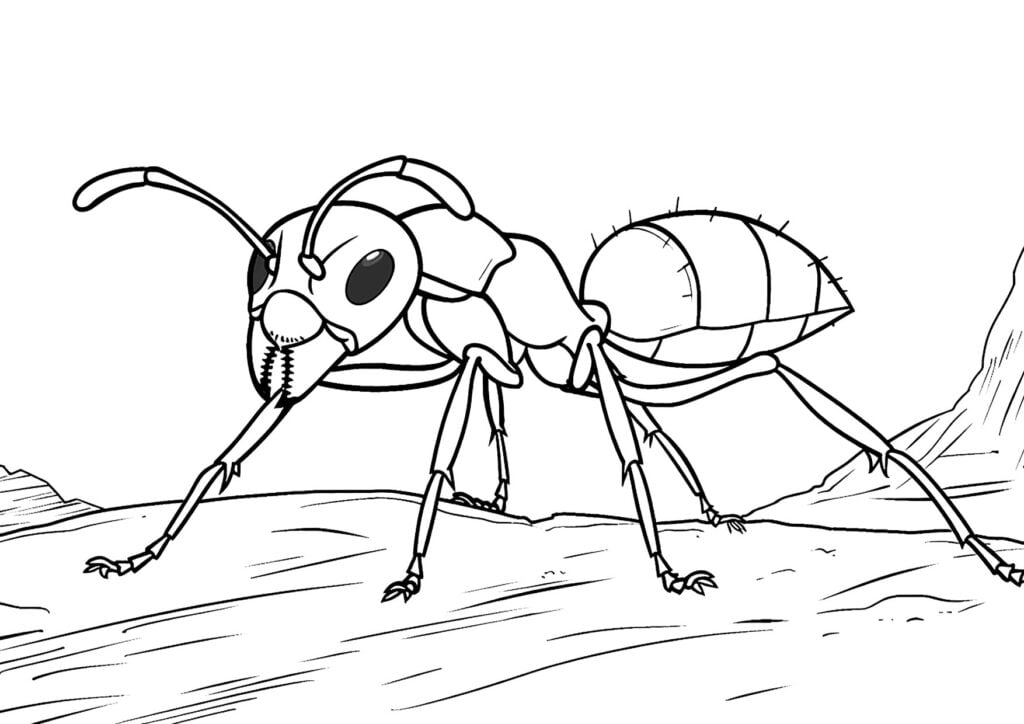
The Mighty Exoskeleton
Ants, like all insects, have a protective outer layer known as an exoskeleton. This isn’t just a shell; it’s a highly efficient structure that provides support and protection. It’s made of a tough material called chitin, which is lightweight yet durable enough to protect ants from their environment.
Tiny but Mighty Muscles
What makes ants such incredible lifters? It’s all in their muscles, which are incredibly strong for their size. These muscles are attached to the inside of their exoskeleton, allowing them to exert great force relative to their tiny body size. This muscle system lets them carry food, build nests, and move quickly to escape predators.
Eyes and Vision
Ants have compound eyes made up of numerous tiny lenses. Although their vision isn’t as sharp as humans, these compound eyes are excellent at detecting movement, which is crucial for spotting predators or finding food. Some ant species that are active during the day rely more heavily on their sight compared to those that are nocturnal.
Antennae: The Sensory Powerhouses
An ant’s antennae are vital sensory organs. They can detect chemicals, air currents, and vibrations. This helps them find food, navigate their environment, and communicate with other ants. Each antenna is loaded with sensory cells that make it an incredibly powerful tool for survival.
Life in the Colony
Each ant in a colony has a specific role, dictated by their physical structure. For instance, the larger, more powerful ants serve as soldiers, protecting the colony, while others will be workers or caretakers of the young.
Join the Fun!
Interested in seeing all these amazing ant features up close? Download our printable ant and get a detailed look at the fascinating anatomy of these tiny creatures. As you color and explore each part, you’ll gain a deeper appreciation for how special and vital ants are to our world. So grab your pencils and start exploring the intricate world of ants today!